I want to be the best-built man in the world, I said frankly,
~Arnold Schwarzenegger, Arnold: The Education of a
Bodybuilder
There are two different types of athletic performance:
1) stamina, and
2) peak output.
Stamina depends on the ability
of your muscles to put out energy for a prolonged period of time. Peak output, on the other hand, is your muscles’ ability to put out a maximum amount of energy over a short time. It is now possible to take old rats—the age equivalent of about 80 years for a human—and rejuvenate some of their athletic performance and coordination back to roughly their young
adult level. We have applied these techniques to a few humans—and to a significant extent they work. There is still a lot to learn about the processes underlying muscular activities,
But, using current knowledge, we have greatly increased our stamina and the size of our muscles with only a few minutes of-exercise a week AND the right nutrients.
The biochemistry underlying athletic performance is, like that of aging, becoming increasingly understood. With current knowledge, it is possible to greatly improve athletic output while decreasing the effort required to achieve that output. For example, you can improve stamina (total muscular output) using the proper nutrients. These techniques apply to young as well as older individuals. It is also a good idea to seek advice from a doctor in the relatively new field of sports medicine. Some useful methods are described below.
The citric acid cycle (also called the Krebs cycle) is the chemical pathway of aerobic (oxygen is required) energy production in animals. Oxygen, the electron donor (the fuel), various enzymes, and various food acids are required.
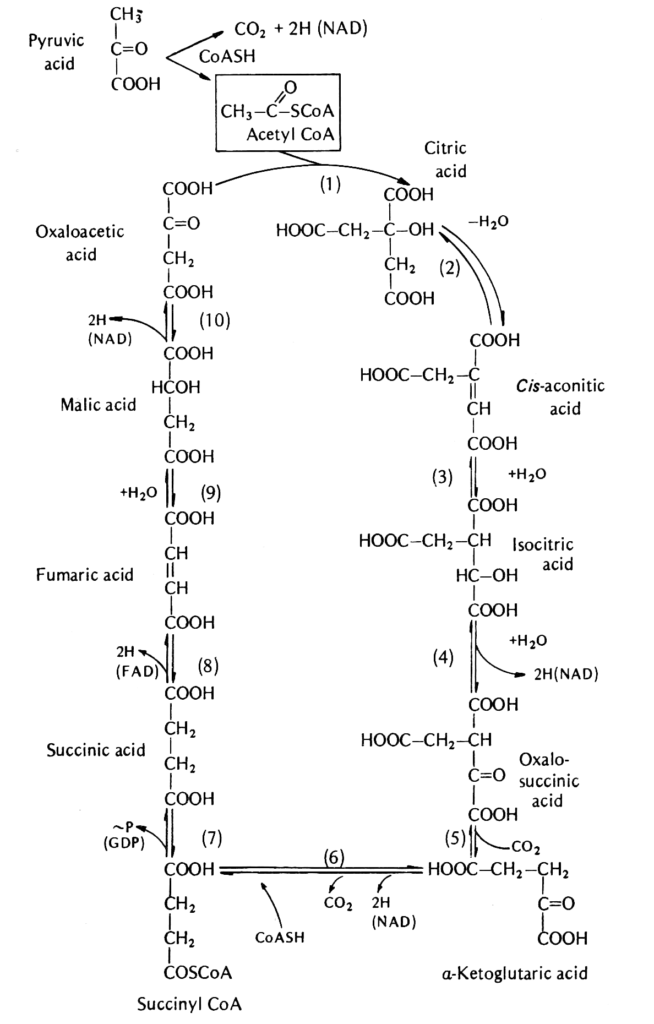
The energy generated by the oxidation of food to carbon dioxide and water in the citric acid cycle is stored in high-energy phosphate bonds of
the ATP molecule (adenosine triphosphate). Energy in the form of ATP is also produced without oxygen via glycolysis. Glycolysis is the primary energy pathway used in short interval high-output athletic events, such as sprints. However, it is not an efficient means of ATP production—only a net gain of 2 molecules of ATP is obtained from each molecule of glucose
metabolized to pyruvic acid, compared to 38 molecules of ATP per molecule of glucose converted to carbon dioxide and water via the citric acid cycle. Moreover, anaerobic (without oxygen) glycolysis produces toxic lactic acid, which causes that burning sensation in fatigued muscles and the mental
confusion which accompanies maximum-output athletics.
Starnina can be increased by increasing the availability of molecules and enzymes used in the citric acid energy cycle: the vitamin pantothenic acid (an essential part of the enzyme acetyl-CoA), malic acid, citric acid, fumaric acid, succinic acid, etc. Nicotinamide or nicotinic acid is also required.
In an experiment with calcium pantothenate (a stable form of vitamin
B-5, pantothenic acid, a required factor in the citric acid cycle), three groups of rats were provided with a diet that was deficient, adequate, or high in calcium pantothenate. The animals were then put in a tank of water at 18 degrees C (64 degrees F) and allowed to swim to exhaustion. Swimming times for the three groups markedly increased with the amount of calcium pantothenate in their diets as follows:
deficient 16 + or – 3 minutes
adequate 29 + or – 4 minutes
high 62 + or – 12 minutes
Experiments on human volunteers subjected to cold water stress agree with these results, Addition of calcium pantothenate also doubled total work output (but not peak output) of isolated perfused frog muscle preparations in separate experiments.
In order to increase stamina with citric acid cycle food acids, doses of a few grams to several grams are required. The compounds are water soluble and, therefore, are excreted rapidly from the body. they can be taken every three or four hours for the duration of the athletic performance.
Hydergine® (Sandoz) is a prescription drug which is effective in slowing down some of the aging processes in the brain. For athletic performance, Hydergine®’s ability to stabilize the brain’s energy metabolism is
relevant. In one series of experiments, blood was withdrawn from anesthetized cats, reducing cerebral blood flow to a critical level; EEG (brain wave) energy values were reduced by 50 percent within 15 minutes.
However, in cats which had been pretreated with Hydergine®, EEG energy was maintained at a normal level for 45 minutes despite the withdrawn
blood. Admittedly, in athletics you aren’t likely to lose much blood, but after long fatiguing effort the oxygen available to your brain will be diminished due to muscular demand. Hydergine® can maintain normal brain energy levels during these stresses, probably resulting in better judgement and superior neuromuscular control. In our experiments, it seems excellent for mountain climbing or any other athletics at high
altitudes (where there is low oxygen availability).
Acetylcholine is a neuromuscular messenger (enables nerves to communicate with muscle cells) and a neurotransmitter (it carries messages between nerves). This chemical is required for muscular control and proper muscle tone. Both lecithin, which contains phosphatidyl choline, and choline can be used by the body to make acetylcholine. Vitamin B-5 (pantothenate} is required for this conversion.
Deaner® (Riker), a prescription drug, increases acetylcholine levels in the brain, where the regulation of movement takes place.
Vasopressin is a hormone secreted by the posterior pituitary gland of the brain. Also called antidiuretic hormone, vasopressin bas several known functions, including the retention of fluids in the body (antidiurctic effect) and pressor effects (blood pressure increases at hundreds of times the
antidiuretic dose), as well as causing contraction of smooth muscle such as intestine and uterine walls and blood vessel walls. In addition, vasopressin has beneficial effects on memory and learning in humans. It increases performance in tests requiring attention, fast reactions, precise visual discrimination, coordination, concentration, and focus. Therefore, we
expect it to be of value to athletes. ‘The effective memory-improving dose is 16 1.U. per day, well below the maximum frequently used antidiuretic dose and far below the pressor (blood pressure increasing) dose. It may be obtained as a convenient nasal spray called Diapid®, a prescription drug made by Sandoz. Possible overdose side effects include brief headaches, pallor, and intestinal cramps, and it sometimes stimulates angina pains in patients with angina pectoris.
CAUTION: People with angina should avoid the use of vasopressin.
- Growth hormone (GED is released by the pituitary gland in the brain in response to exercise, fasting, hypoglycemia, sleep, trauma, dopaminergic stimulants, and other factors. It has many functions, including maintaining the immune system, stimulating muscle growth, and burning fat. Exercise in which there is briefly sustained muscular peak output releases growth hormone; exercise at less than peak effort, even when prolonged, releases little or no GH. Recent evidence (from the Baltimore Longitudinal Study of Aging) indicates that growth hormone release in response to exercise ceases by the
age of 30 or so, however, although GH release in response to
other factors continues. Jogging usually involves less than peak output and, therefore, usually results in no release of GH. As noted earlier, some recent research has found higher HDL levels in runners. HDL (high density lipoprotein) is a fraction of fat-protein compounds in the blood that provides a reduction of risk of heart attacks. However, the studies have not compared the HDL levels before subjects began running to HDL levels after becoming runners. It is possible that runners may have a high HDL to begin with; we do
know that runners tend to be highly educated, well nourished, health-oriented, lean nonsmokers, who are generally free of disorders such as hypertension. Since lazy obese people rarely choose to become marathon runners, some of these apparently pro-running results may be caused by subject selection bias.
There are several nutrients and prescription drugs which cause GH release. These include the amino acids arginine and ornithine and the prescription drugs L-Dopa (another amino acid), bromocriptine (Parlodel®, by Sandoz}, and vasopressin (Diapid®, Sandoz nasal spray). In one study, 1/4 gram per day of L-Dopa increased the growth hormone output of men in their 60s (who were not suffering from Parkinson’s disease)
GROWTH HORMONE CAUTION: Inappropriate use of GH releasers may have adverse consequences. They should not be used by persons who have not completed their long- bone growth (that is, who have not grown to their full height) unless they have been advised to do so by their physician.
After full height is attained, GH will not cause further height increases. Excess GH will cause the skin to grow so rapidly that it becomes noticeably coarser and thicker; this effect is reversible when excess GH is withdrawn. Very excessive GH over an extended period of time can cause irreversible enlargement of joint diameter (which may be unsightly but is usually not dangerous) and lowering of voice pitch due to larynx growth. The maintenance of extremely high levels of growth hormone (above normal teenage to young adult levels) for extended periods of time requires further safety research. In some GH releaser experiments on animals either
previously or subsequently given cancer, the GH releasers usually caused an improvement. At Cornell University Medical Center, however, hypophysectomy (surgical removal of the hypothalamus) in women with advanced metastatic breast cancer has sometimes produced dramatic improvements.
Since this procedure affects many other hormones besides GH, including LHRH, LH, FSH, TRF, TSH, thyroid, prolactin, estrogens, progestins, endorphins, beta lipotropin, etc., it is not yet clear what is going on here.
In recent research, it was found that L-Dopa given to old rats could restore their swimming abilities to that of young adult rats. The old rats, before getting L-Dopa, swam in a more vertical position and used the energy they did have in a very inefficient manner, sinking under the water after a rel-
atively short time. The old rats, after getting L-Dopa, swam in a more horizontal position (like the young rats) and were indistinguishable from the young rats in their swimming performances, L-Dopa is used in the brain to make dopamine and norepinephrine. Dopamine is a major neurotransmitter involved in motor (muscular movement) control. Parkinson-ism patients, who have lost their fine motor control and developed tremors, are often benefited by L-Dopa or other dopaminergic stimulants. (In many cases, a combination ofbromocriptine [Parlodel®, Sandoz} plus a somewhat reduced dosage of L-Dopa provides better control of Parkinsonism with fewer side effects.) I-Dopa, like other catechols, is a
good antioxidant and has been used for radiation protection.
CAUTION: Long use at high dose levels, especially without adequate intake of other antioxidants, can lead to undesirable autoxidation side effects.
- Proteolytic enzymes—enzymes that dissolve proteins— increase the turnover rate for proteins by stimulating protein manufacture and repair. Examples of common proteolytic enzymes are bromelain (in raw pineapple) and papain (in raw papaya). Cooked or canned pineapple and papaya do not contain these enzymes, which are destroyed by heating. These enzymes can slowly dissolve away damaged protein tissues, speeding up healing and repair. They have been used to reduce inflammation and edema and to treat many athletic injuries. If you eat raw pineapple or papaya for these enzymes, watch out for the development of sore and tender corners of
your lips (they are tenderized in the same way that proteolytic enzymes tenderize meat). When this occurs, stop eating these fruits. Promptly washing your mouth after eating raw pineapple or papaya is a good idea, if you eat them frequently. CAUTION: Do not eat raw pineapple or papaya if you have an ulcer. Athletes frequently take tablets of Ananas: (Rorer), a prescription form of bromelain, for athletic injuries.
It has been observed that women athletes sometimes stop menstruating. Recently, Harvard researchers suggested a possible reason. They noted that girls at the start of menstruation need to have a body fat content of about 17 percent or menstruation will not begin. When nonathletic women lose 10 to
15 percent of their body weight, including about a third of their body fat, they usually stop menstruating. The researchers suggest that this may be an adaptation to prevent skinny women from becoming pregnant, because until recently an adequate body store of fat was necessary to survive food
shortages, which were frequent.
Athletic injuries are common. DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide) is very helpful in reducing damage in many injuries. In crushing injuries, including bruises, blood leaks into the damaged tissues. When the red blood cells hemolyze (break down), they release copper and iron, which stimulate the production
in these injured tissues of free radicals.
DMSO is an especially effective scavenger of a particular type of free radical, the hydroxyl radical. When DMSO (a clear liquid) is placed on the
skin over the injury, it actually moves through the skin and into the deeper tissues, where it inhibits destruction by free radicals, allowing healing to proceed more rapidly. DMSO has been used successfully in some cases of spinal cord injury where, if a solution in physiological saline is injected soon enough (within a few hours after the injury), it has helped
prevent the development of paralysis. DMSO is available as a prescription drug and is also sold in some health food stores.
Be careful that you buy a high-purity grade of DMSO
Biochemistry has a great deal more to offer the athlete, whether amateur or professional. It is actually possible to remodel your body, adding muscles and eliminating fat, with far less effort than with conventional means. The aging effects that eventually end all athletic careers can be delayed for at
least several years, and perhaps for decades.
Comments (0)